JEE MAIN CHAPTER OVERVIEW
Chapter Priority | 1 (HIGHEST) |
Number of problems in PYQ | HIGH |
Difficulty | EASY |
KEY CONCEPTS FOR JEE MAIN
LAW OF GRAVITATION
Gravitation force between two particles is given by:

Force is attractive and acts along line joining the two particles. Both objects pull each other with same force.
Force is Conservative.
G is a constant, called the universal gravitational constant.
PRINCIPLE OF SUPERPOSITION
When there is a system of masses, total gravitational force on any particle is the vector sum of the gravitational force applied on that particle by all other particles.

JEE MAIN EXAMPLE QUESTIONS
QUESTION: Find force on ‘2m’ mass. Given that masses are at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side L.
We need to add the forces on ‘2m’ due to both the ‘m’ masses vectorially.

QUESTION: Two particles of equal mass ‘m’ move in a circle of radius ‘r’ under the action of their mutual gravitational attraction. The speed of each particle will be :
(JEE Main – 2023)

[If you cannot solve on your own, let us know your doubt at www.savai.co.in or WhatsApp me @ 7982286138, we will send solution.]
NULL POINT
Another common question comes to calculate Null point.
The point where force on a particle kept between two masses is zero.
In the figure below, find the point where net force on a particle will be zero between the line joining the two masses. Distance between the centers of the two masses is ‘L’.

Note: Before null point, net force is towards 9M mass and after null point net force is towards 4M mass.
GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL ENERGY
Gravitational Potential Energy between two masses kept at a distance ‘r’ from the each other is

Here, we take reference point as infinity where potential energy is zero.
TOTAL POTENTIAL ENERGY OF A SYSTEM OF MASSES
To find PE of a system, write down the PE between all pairs of masses and add them up to get the PE of a system. Let us see an example:
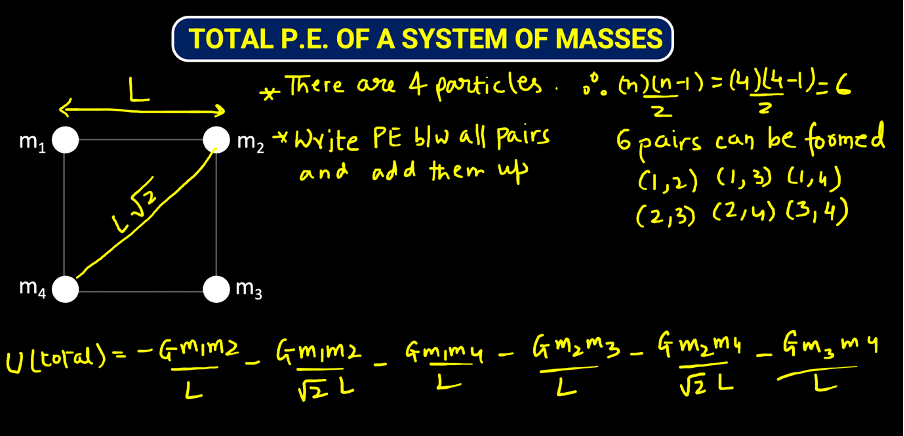
JEE MAIN Question:
A body of mass is taken from earth surface to the height h equal to twice the radius of earth (Re), the increase in potential energy will be (g = acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Earth)
[HINT: When talking about a point outside a planet, assume planet is a particle of radius r. Then find out the potential energies in initial and final case]
[If you cannot solve on your own, let us know your doubt at www.savai.co.in or WhatsApp me @ 7982286138, we will send solution.]
MINIMUM VELOCITY TO CROSS FROM ONE PLANET TO ANOTHER PLANET
Note: This is not escape velocity. We will discuss escape velocity in these notes also.
Remember: Gravity is conservative. If only gravity is acting between particles, we can conserve mechanical energy.

Do not make the mistake of taking v = 0 when particle reaches 4M mass. That will not give us the minimum velocity at 9M mass.
GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL
It is defined as potential energy per unit mass.
Its SI units are “Joule/Kg”. It is a scalar quantity.
When potential at a point due to a mass ‘M’ is V and another particle ‘m’ is kept at the point, the potential energy of the system becomes U = mV.
You have to remember various bodies for which potential is asked in JEE Main. All such cases are given later in this document.
Potential due to a point mass:
For a mass M, gravitational potential at a distance ‘r’ from it is:
GRAVITATIONAL FIELD
Gravity acts at a distance and does not need the bodies to be in contact. In order to study such forces, scientist define a field.
Gravitational field is force per unit mass. Its SI units are ‘m/s2’ (same as that of acceleration). In fact, ‘g’ is the field of gravitation due to earth on the surface of earth.
When field at a point due to a mass ‘M’ is E and another particle ‘m’ is kept at the point, the force on ‘m’ is F = mE
Field is a vector quantity. It has energy and momentum of its own.
For a point mass, the gravitational field is
POTENTIAL & FIELD FOR SPECIAL CASES
It is important to know the formulae and graphs for Potential and Field for various bodies like:
a. Point Mass
b. Ring
c. Hollow Sphere
d. Solid Sphere
These are given below:
POINT MASS

Please take note of the graphs also. Sometimes these are asked directly in JEE MAIN.
RING

HOLLOW SPHERE

SOLID SPHERE

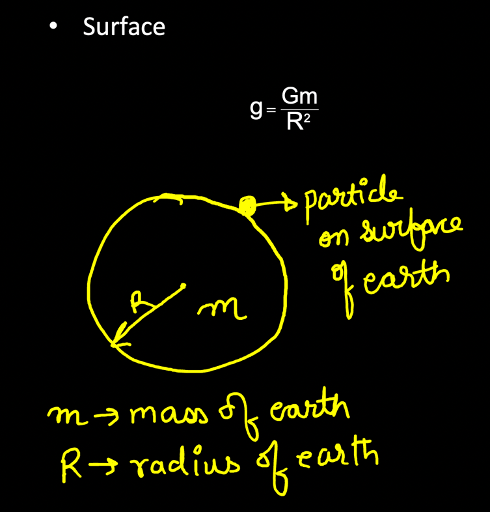
geffective
We can use the Gravitational field formula for solid sphere to find out effective acceleration due to gravity both above the surface at a height H and below the surface at depth ‘d’.
Remember,
geffective at surface is
geffective at depth (d)
Note: g decreases with depth

geffective at height (H)

When H<<R, then effective g:
geffective due to Rotation of Earth
g changes due to rotation of earth. It is minimum at equator and maximum at poles.

JEE MAIN Question
At a certain depth ‘d’ below surface of earth. Value of acceleration due to gravity becomes four times that of its value at a height 3R above earth surface. Where R is radius of earth (Take R = 6400 km). The depth d is equal to (JEE Main 2023)
(A) 5260 km (B) 640 km (C) 2560 km (D) 4800 km
[Hint: Use the formulae given above for depth and height.]
[If you cannot solve on your own, let us know your doubt at www.savai.co.in or WhatsApp me @ 7982286138, we will send solution.]
ESCAPE VELOCITY
It is the minimum velocity required for an object to escape from the gravitational pull of the earth and reach infinity.
It is derived by conserving energy between a point on earth’s surface and infinity. At infinity both potential and kinetic energy are assumed to be zero.

Questions asked in JEE MAIN play with the formula – They can change the radius of the planet, mass of the planet or give density of the planet. Ratios are often asked when radius, mass or density is doubled or tripled. Just substitute the values of new radius, mass, density in above formula to get new value of escape velocity.
Remember,
JEE MAIN Question
A planet having mass 9 Me and radius 4Re, where Me and Re are mass and radius of earth respectively, has escape velocity in km/s given by :
(Given escape velocity on earth Ve = 11.2 × 103 m/s) (JEE Main 2023)
(A) 67.2 (B) 16.8 (C) 33.6 (D) 11.2
[If you cannot solve on your own, let us know your doubt at www.savai.co.in or WhatsApp me @ 7982286138, we will send solution.]
SATELLITE
Speed of satellite and time period of satellite are favorite topics of JEE MAIN. Especially time period and radius of orbit relationship.
To find speed, equate gravitational force with centripetal force required to keep satellite in orbit of radius ‘r’.
Velocity of satellite does not depend on mass of satellite but only on radius.
Velocity of satellite is given by the formula:
A lot of questions are asked on time period and radius relations in JEE MAIN. They will change the radius and ask the ratio of old and new time period.
The relation between time period and radius of satellite is:
Which can also be written in the form:

Try this question:
The time period of a satellite of earth is 24 hours. If the separation between the earth and the satellite is decreased to one fourth of the previous value, then its new time period will become.
(A) 4 hours (B) 6 hours (C) 12 hours (D) 3 hours
[If you cannot solve on your own, let us know your doubt at www.savai.co.in or WhatsApp me @ 7982286138, we will send solution.]
GEOSTATIONARY SATELLITE
Satellites that are placed in an equatorial plane at a height of approximately 36000km above the earth have the same time period of rotation as the earth (i.e. the move on circle in 24 hours). This means that they stay over one spot of the earth on the equator.
They have the same time period and therefore the same angular velocity of rotation as the earth.
ENERGY OF A SATELLITE
A satellite will have both kinetic and potential energy. Sum of potential and kinetic energy is total energy. These depend on the radius of orbit in which satellite is rotating.

Questions asked in JEE MAIN are on the amount energy need to change the radius of satellite from r1 to r2. In these questions, remember to use total energy formula and not just the potential energy. Energy needed is:
(Final total energy – Initial total energy)
KEPLER’S LAWS
1st Law: All planets move along an elliptical orbit with sun at one of its focus.
2nd Law: Area swept by the line joining the sun and the planet sweeps equal areas in equal intervals of time
3rd law: Square of the time period of a planet is proportional to the cube of the length of the semi major axis of its orbit

In the second law, keep in mind the aerial velocity is constant as angular momentum of planet around sun is constant. Angular momentum about sun is constant because gravity acts along the line joining sun and planet and thus its torque about sun is zero. When torque is zero, angular momentum will remain constant.
Angular momentum is a constant given by
where, L and m are the angular momentum and mass of planet.
Hope you can REVISE GRAVITATION FOR JEE MAIN PHYSICS from this guide to answer all varieties of JEE MAIN PYQs. Thanks a lot!
[If you cannot solve any doubts related to any chapter of physics, upload a photo of your doubt at www.savai.co.in or WhatsApp me @ 7982286138, we will send solution.
If you want to get in touch for guidance related to JEE, career etc. I am always available at the at www.savai.co.in or WhatsApp me @ 7982286138
Please share www.savai.co.in in case you find our content helpful.]


Comments