KINEMATICS for JEE MAIN
- Aniket Verma
- Jan 23, 2024
- 4 min read
JEE MAIN CHAPTER OVERVIEW
Chapter Priority | 1 (HIGHEST) |
Number of problems in PYQ | HIGHEST |
Difficulty | EASY |
To solve JEE MAIN problems for KINEMATICS, you need to remember all formulae given in these notes.
Note: Questions in the exam are easy if you know the concepts well. Focus on practicing formula applications as without memorising formulae, the questions can become calculation heavy.
FRAME OF REFERENCE
Motion is a combined property of object and observer
A frame of reference is the point from where motion is observed.
We can choose a frame of reference and axis based on our convenience.
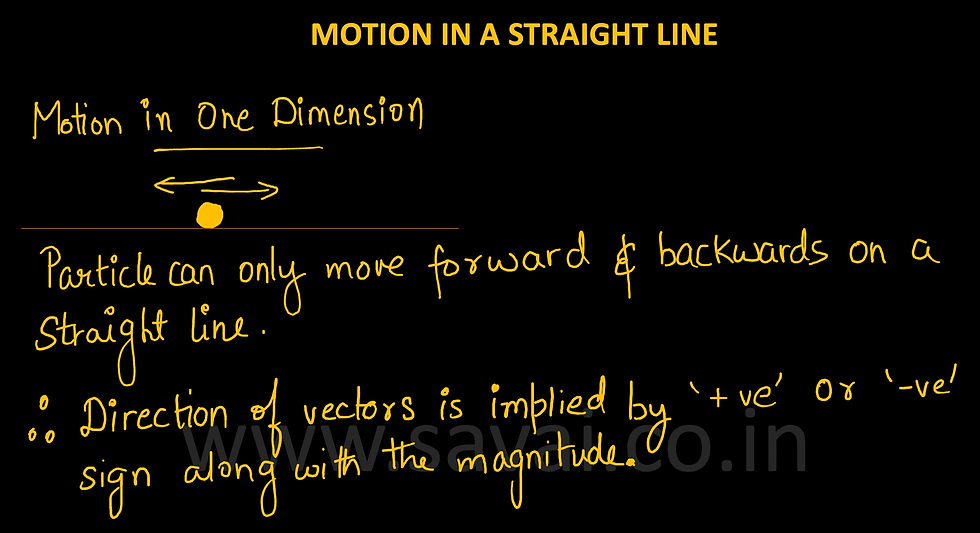
MOTION
An object is said to be in motion if it continuously changes its position with respect to a frame of reference.
We describe motion by the following quantities:
Distance
Displacement
Speed
Velocity
Acceleration
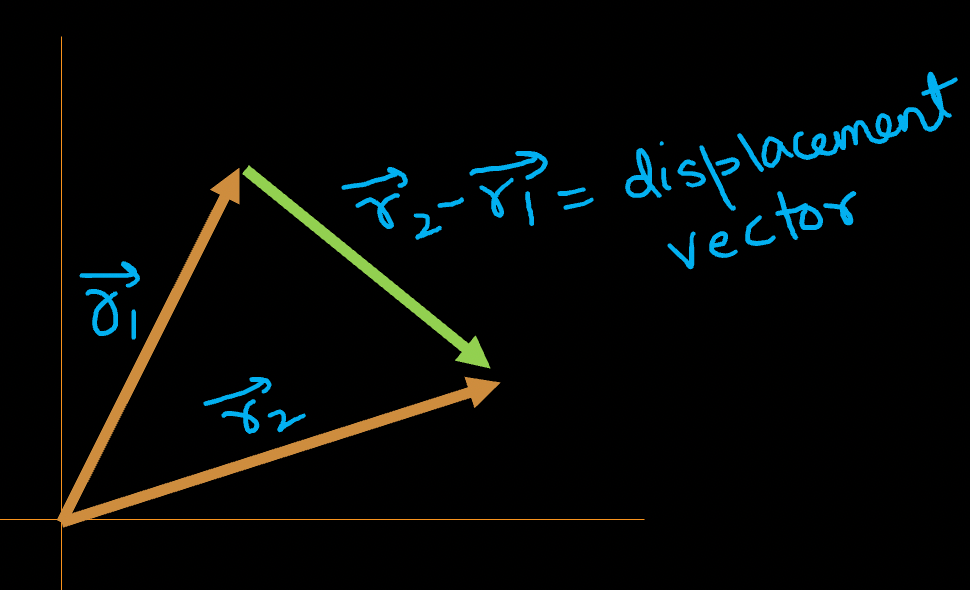
POSTION VECTOR
We can define a vector from the origin of the frame of reference to the point(particle) we are observing. That vector is called the position vector.
DISTANCE
It is the actual length of the path travelled by a particle.
Scalar
Dimensions: [L]
SI unit: meter
If particle moves, it is always non-zero
DISPLACEMENT
It is the shortest distance between the initial and final positions of a particle.
•Vector
•Dimensions: [L]
•SI unit: meter
•If particle moves, it can be zero for motion in a closed loop
SPEED
Average Speed = Total Distance/Total Time
Instantaneous Speed at any point C (speed of particle when it is at point C)
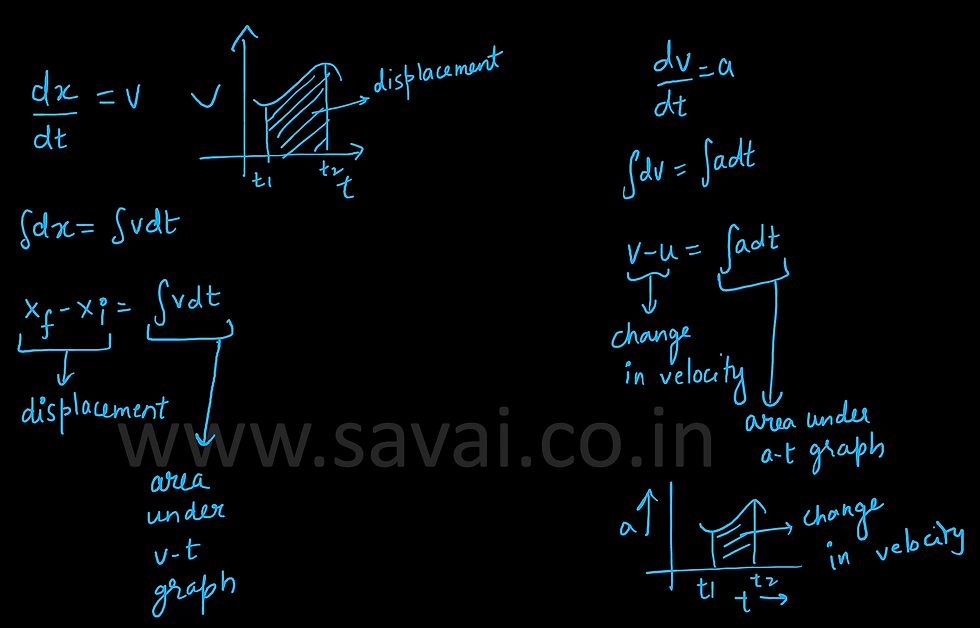
Instantaneous speed (v) = dr/dt
VELOCITY
Average Velocity = Total Displacement/Total Time
Instantaneous velocity at Pt. 3 (velocity of particle when it is at point 3)
ACCELERATION
Average Acceleration = Change in Velocity/Total Time
Instantaneous acceleration at C (acceleration of particle when it is at point C)
Speed, Velocity and Acceleration
TRY A JEE MAIN PYQ
Q. The position of a particle as a function of time t, is given by x(t) = at + bt^2 – ct^3 where, a, b and c are constants. When the particle attains zero acceleration, then its velocity will be:
MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
MOTION WITH CONSTANT ACCELERATION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
Proof: v = u + at
Proof: s = ut + (1/2)*at^2
Proof: v^2 - u^2 = 2as
Some Important points
TRY A JEE ADVANCED PYQ
A car starting from rest accelerates at the rate f through a distance s, then continues at constant speed for time t and then decelerates at the rate f/2 to come to rest. If the total distance traversed is 15 s, then s = ?
[Do visit www.savai.co.in for FREE DOUBT SOLVING, if you face trouble in above question]
VERTICAL MOTION
•Acceleration due to gravity ‘g’ = 9.8 m/s^2 is assumed to be constant.
•We take a direction (upward or downward) as positive as per convenience. Note: Make sure to follow the same direction convention for the entire problem.
•Since ’g’ is constant, we can use equations of motion.
We ignore air resistance in problems of vertical motion
SIGN CONVENTION
•It is extremely important to understand sign convention for vertical motion problems.
•It does not matter which direction you choose as the positive direction as long as all vectors in the problem are assigned proper signs (+/-) and the same sign convention is followed throughout.
VERTICAL MOTION CASE 1:
Ball thrown up from ground with velocity 'u'
Time to reach top
Max height
Time to reach back to the ground
SOME IMPORTANT INFERENCES
•Upward and downward motion of the particles are symmetrical.
•It takes same amount of time in first half of journey and second half of journey.
•Speed of the ball at the same height is same in first and second half (only direction is opposite)
•Except for the top, a particle reaches the same height twice.
•Let’s say time at which particle reaches height h are t1 & t2. Then:
•t1+t2 = 2u/g = Total time of flight
MOTION IN A PLANE
When acceleration is constant:
The problem of motion in a plane can broken down into two independent problems of straight line motion, one along the X-axis and the other along the Y-axis.
PROJECTILE MOTION
When a particle is thrown obliquely near the earth’s surface, it moves along a curved path. Such a particle is called a projectile and its motion is called projectile motion.
BEST WAY to study projectile motion is to break it into two part along x & y axis
Velocity vector in projectile motion:
Analysis of Projectile Motion
TIME OF FLIGHT for PROJECTILE
RANGE
MAXIMUM HEIGHT
For complimentary angles of projection,
T1 and T2 are time of flights for complimentary angles.
H1 and H2 are heights of projectile for complimentary angles.
EQUATION OF TRAJECTORY
Trajectory means the path of the particle. It removes the variable of time from the equations and expresses y-coordinate of the particle as a function of x-coordinate.
SUMMARY OF PROJECTILE MOTION
PROJECTILE ON AN INCLINE PLANE
PROJECTILE DOWN THE INCLINE
RELATIVE VELOCITY
The concept of relative motion arises when we want to observe motion of a body from a moving body.
If we want to analyze the motion of B from point of view of A then first reverse (i.e. put a -ve sign) in motion of A (-rA, -vA, -aA) then add them with motion of B (rB, vB, aB) to get relative motion of B w.r.t A
( rB – rA , vB – vA , aB – aA )
RAIN-MAN or RAIN-CAR PROBLEMS
In such problems, you will be given the velocity vector of rain falling down which can be vertical or at an angle on the ground. You will also be given the velocity vector of an object(man or car) on the ground and you will be asked to calculate the relative velocity of rain with respect to object.
THE BEST WAY to solve such problems is to draw a vector diagram.
Remember the formula in the image below:
A common question is the angle at which man should hold umbrella. It is solved below:
RIVER SWIMMER PROBLEMS
A category of questions where a swimmer swimming in the river has to cross it. Remember, in such questions the BEST WAY is to draw the vector diagram of the velocities.
NOTE: In the questions, the "velocity of the man in still water" means velocity of man w.r.t river
See the image below and learn the diagrams properly
Some calculations are often asked
Please see the images below:
Time to cross river, horizontal drift & total distance travelled
Shortest time to cross the river
Angle to swim for shortest distance to cross river and time associated with it
Thanks a lot!
If you want to get in touch for guidance related to JEE, career etc. I am always available at the at www.savai.co.in or WhatsApp me @ 7982286138
Please share www.savai.co.in in case you find our content helpful.]

















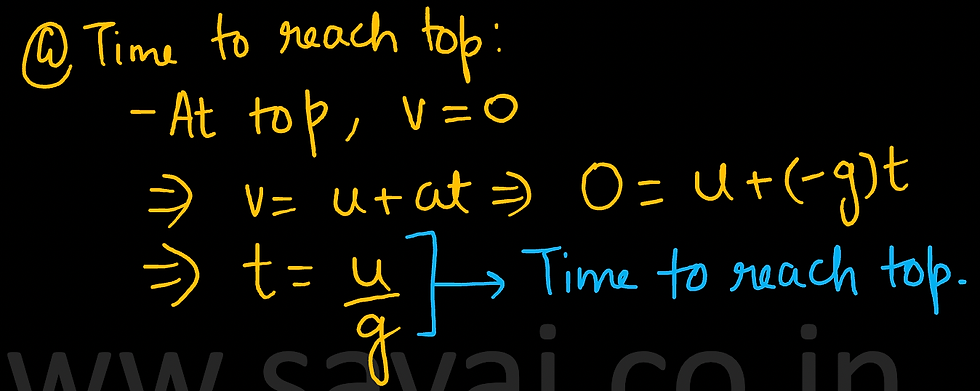




























Comments